The difference between Persuasive design and Nudging
Designing for persuasion is not the same as designing for digital nudging. Though both may use some similar tactics, they are two distinct approaches with different goals.
In this blog post, we'll explore the difference between persuasive design and digital nudging. We'll look at the different goals and objectives of each approach, as well as some of the common tactics used.
Read More
Choice architecture
It's estimated that the average adult makes about 35,000 decisions a day and over 200 are related to food. So decision fatigue is a real problem for users. This is why the food industry has options such as a set menu, buffet and la carte to help us decide what to eat. UX design also has similar strategies.
Read More
Persuasive design strategies for better user engagement
What happens when users don't behave the way you expect them to? What if your users are exhibiting toxic behaviour, bullying or simply not engaging with your product? In this post, i'll explore some ways to change user behaviours in UX design both in video games and apps.
Read More
What are affordances and how can they Improve Player Experience?
An Affordance in simple terms is a clue as to what actions are possible in order to use something. For example, wheels on a bike or the handle on the door give you an affordance as to how to use it. These are simple examples but games can be complicated to understand with their changing states and different play styles and controls.
Read More
Combating toxic user behavior
Video games and social media can be great escapes from our daily lives but can also be an outlet for the dark sides of our personalities. This is why designers need to find ways of dealing with toxic behaviour by creating features and mechanics that discourage it, such as reporting systems and mute buttons.
Read More
Why you should use progressive disclosure.
Progressive disclosure is a design strategy that allows users to gradually learn about important features in a step-by-step process. It is an effective way to reduce cognitive load and reduce the learning curve so users feel comfortable with the level of information they are viewing, without feeling overwhelmed or frustrated.
Read More
How to overcome choice paradox
At its core, UX design is about solving problems. And yet, when it comes to designing user interfaces, we often face a dilemma: too many choices can paralyze us, but too few can leave us feeling unfulfilled. How do we find the right balance?
Read More
The principle of learned helplessness
It is necessary to guide users through new experiences to prevent them from becoming frustrated or lost. However, this can lead to excessive hand-holding that ruins the gaming experience by removing the sense of agency and can lead to players becoming passive viewers in an interactive experience.
Read More
How games teach through play
Some games have great tutorials and some are innovative whiles some are so bad they become memes. Teaching users how to play your game can make or break player experience. In this post, I will explore some of the best ways of understanding players learning styles and some tutorials and teaching mechanics found in games.
Read More
Navigation UX: Cyberpunk 2077
I recently revisited Cyberpunk 2077 on PC and I can say that it’s in a much better place than when it launched. However, during my play, there were a number of UX and UI inconsistencies that I noticed. And this goes to show how complex it is to make AAA games even with all CDPR’s past experience of making ground-breaking open-world RPGs. A great user experience should be like a butler, only there when you need it. But unfortunately, when it goes wrong, it really stands out.
Read More
Trends: Player as Director
We have seen some impressive leaps in innovation such as the Nemesis System and the release of UE5 which are all important for us to understand in order to craft strategies for this fast-changing industry. We have also seen disruption within the movie industry and now many analysts are predicting that the streaming wars will eventually push companies to look into subscription-based gaming models to find growth. But when does a movie become a game and a game become a movie?
Read More
The Mechanics, Dynamics, and Aesthetics Framework
The MDA framework is an important framework for thinking about games from both a designer’s and the players’ point of view and was developed by Marc LeBlanc and Robert Zubek. It’s a helpful framework to understand when developing and designing games or even introducing gamification elements to your product.
Read More
Change Your Damn Story
Look, we all have stories we tell ourselves. Some are useful, most aren’t. And let’s be honest: a lot of the stories we carry around are total crap. They’re excuses dressed up as truth. They’re the reason you stay small, keep quiet, and avoid the big stuff.
Read More
Play Personas: Lean in, Lean forward, Lean back and Lean out.
In Ahmed Salama the Game UX Summit 2019 talk, he laid out his ideas for play-based personas and how they can be applied during the design process for AAA games. A useful insight that can be a good tool for all designers throughout the industry to be aware of and to add to their repertoire when it comes to catering for the user’s Cognitive abilities during different Phases of play.
Read More
Why Video Games Are Basically Just Big Science Experiments: Positive and Negative reinforcement
Giving users feedback is an important part of any digital interaction. Behavioural learning is a theory that suggests that the use of reinforcement leads to its continued occurrence. This theory is often used in video games to reinforce certain behaviours or weaken them through the use of feedback loops.
Read More
The Psychology Behind Game Reward Systems
Game reward systems can also be used to facilitate goal setting and achievement. By providing rewards for achieving specific goals, players are motivated to focus on these goals and work toward accomplishing them. This approach not only promotes skill development but also helps to promote a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction with the game.
Read More
The Kobayashi Maru Lesson: Thinking Outside the Box
In the world of Star Trek, The Kobayashi Maru was a test designed to test how individuals handle an impossible situation. Kirk's reprogramming of the scenario showed that he could think outside the box and find a way to succeed where others had failed. Additionally, in real-world scenarios, the ability to find loopholes and innovative solutions to problems is often a highly valued skill.
Read More
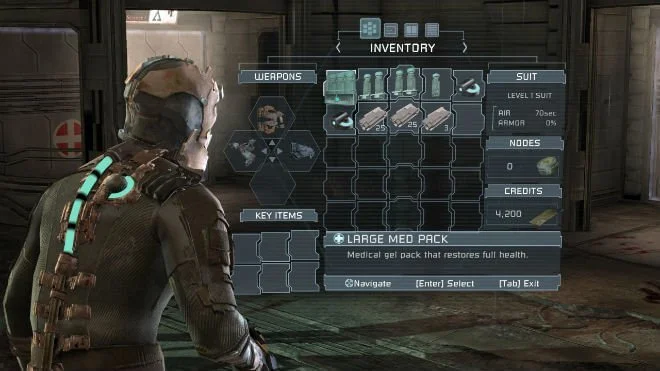
The diegetic UI of Dead Space
Dead Space is a sci-fi horror game, where you play as Isaac Clark an engineer stuck on The Ishimuram, a ship infested with space zombies. Your job is to fix that vessel and find your girlfriend. To maximize the playing horror experience the designers crafted a fully diegetic UI that has become very influential in the gaming industry.
Read More
Accessibility in The Last of Us Part II
With millions of gamers facing difficulties and barriers, whether temporary or long term. Developers are seeking better ways to provide ways remove these barriers. Naughty Dog's The Last of Us Part II has been praised for its industry-defining accessibility features. So what can we learn from it?
Read More
Elden Ring and The psychology of gains and losses
The more difficult something is to achieve, the more people like it. This may be counterintuitive from a UX designer’s perspective as we often strive for the easiest most friction-free experience possible. But people play games for the challenge. In fact, games often introduce harsh limitations on players and put them through difficult situations. Non more so the Souls series of games by FromSoftware.
Read More